August, 2005
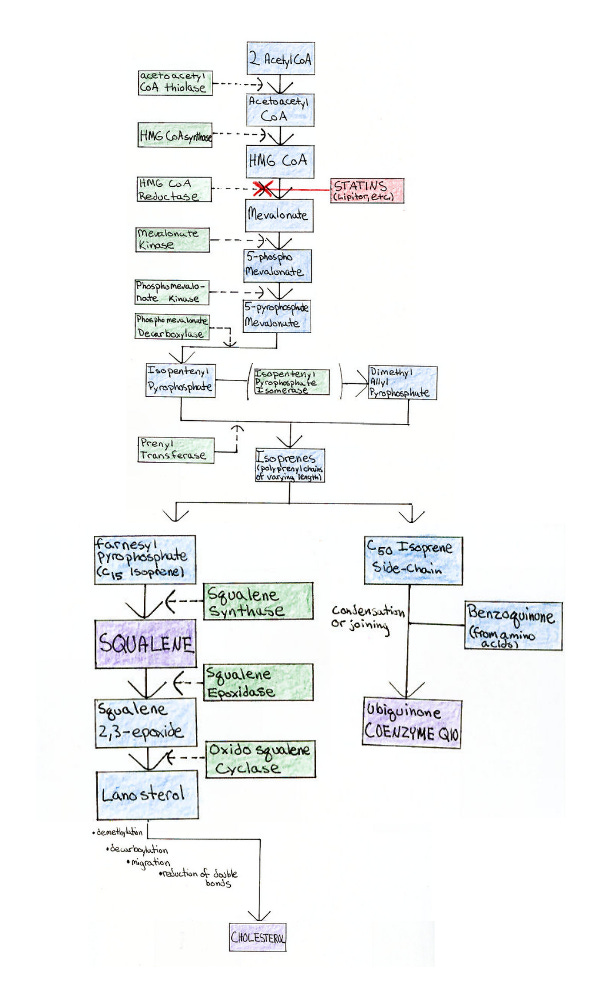
The flow chart below shows how the body biosynthesizes cholesterol. Acetyl CoA is a product of the metabolism of any source of energy — be it protein, fat, or carbohydrate.
Acetyl CoA is then changed into various other products (shown in blue) by numerous enzymes (shown in green), until it is converted into several important end products (shown in purple).
Note that statin drugs — the popular "cholesterol-lowering" drugs such as Lipitor, Mevacor, Zocor, Lescol, Pravachol, etc., shown in red, inhibit the synthesis of mevalonate. Mevalonate is not only the precursor of cholesterol, but also the precursor of squalene and coenzyme Q10 (ubiquinone), two very important compounds.
In order to read the flow chart, please maximize your browser window with the button in its upper-right corner, and then scroll this page to the right until the nav bar is no longer showing.
You can click on the coenzyme Q10 end product shown below, as well as the squalene end product to learn more about the role of these essential nutrients in the body. You can click on isoprenes to learn more about the many different isoprenes and their importance to the body.
One specific isoprene, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate, activates the enzyme Rho, which may contribute to atherosclerosis. Rho activation is given its own page.
Clicking on cholesterol will bring you to a flow chart showing the synthesis of vitamin D, bile acids, and steroid hormones from cholesterol.